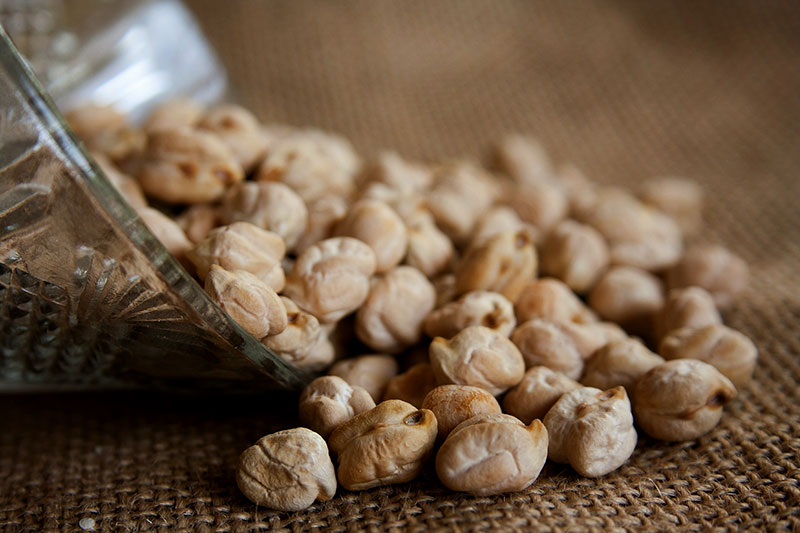
Chickpeas (Garbanzo)
The Chickpeas (Garbanzo) are an annual legume. It belongs to family Fabaceae and subfamily Faboideae. The botanical name of chickpea is Cicer arietinum. Different types of chickpeas are found all over the world. These are variously known as gram or Bengal gram, garbanzo or garbanzo bean, Egyptian pea, chana, and chole. Seeds of chickpeas are protein-rich. Know Chickpeas (Garbanzo) Nutrition facts and Health benefits Chickpeas in this article.
Chickpeas can be ground into flour to make falafel. It is also used to make salads, soups and stews, curry and other meal products. It is important in Indian and Middle Eastern cuisine.

Nutrition facts Chickpeas
Chickpeas are dense in nutrients. They provide rich content of protein, certain dietary minerals like iron and phosphorus, folate and dietary fiber. It also contains a moderate amount of thiamin, vitamin B6, magnesium and zinc. According to the reference levels established by the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization and World Health Organization, proteins in germinated and cooked garbanzo are rich in essential amino acids such as lysine, isoleucine, tryptophan, and total aromatic amino acids.
Effects of Cooking
A serving of 100g of cooked chickpeas can provide 164 kilocalories (690kJ). These cooked chickpeas contain 60% of water, 27% of carbohydrates, 9% protein, and 3% fat. Cooking can increase the quality of protein by inactivating or destroying heat-liable anti-nutritional factors.
Cooking can also increase the digestibility of proteins, essential amino acid index, and protein efficiency ratio. It can also significantly reduce fat and mineral content.

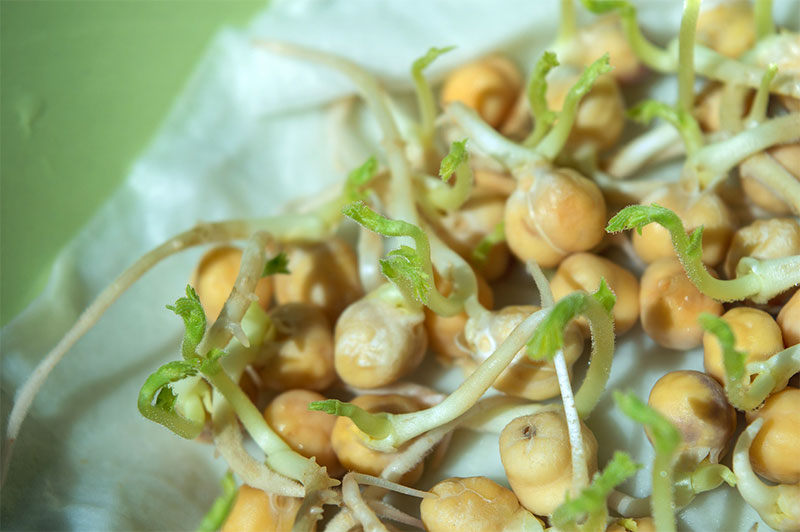
Germination
- Germination of chickpeas improves the digestibility of proteins but it occurs at the lower level than cooking. Chickpea germination improves crude protein by degrading protein to simple peptides. It improves crude protein, non-protein nitrogen, and crude fiber content. Germination can decrease the amount of tryptophan, lysine, sulfur, and total aromatic amino acids.
-
Minerals and vitamin B when cook, use germination to maintain it effectively.
- Stachyose and raffinose are the oligosaccharides that can be reduced in higher amounts through germination than through cooking. Phytic acids can also be decreased significantly.
Leaves
People eat vegetables of their leaves. Chickpea leaves can supplement more dietary nutrients to the malnourished populations. garbanzo leaves have a significantly higher mineral content than either cabbage leaves or spinach leaves. But nutrient availability and environmental factors can influence the content of minerals.
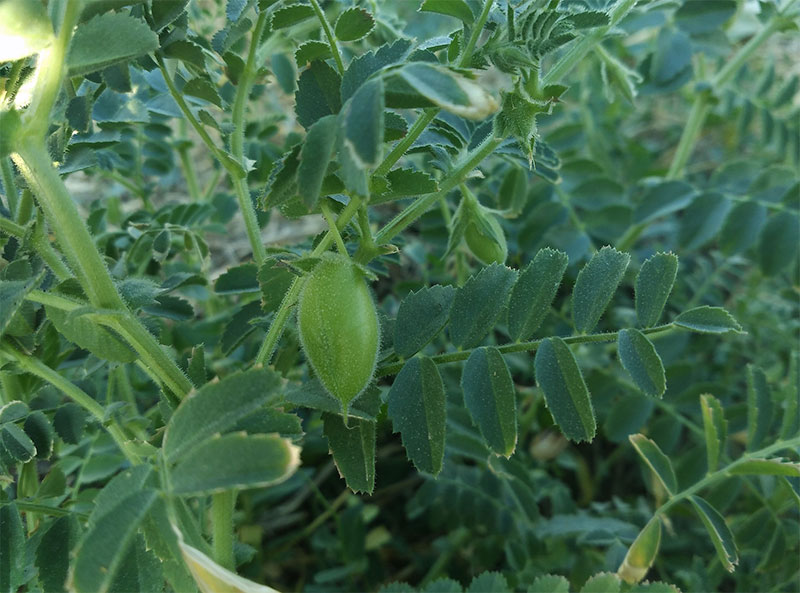

Also Read: How to grow chickpeas.
Nutritional value garbanzo per 100gm
Energy 686 kJ (164 kcal)
Carbohydrates 27.42 g
Sugars 4.8g
Dietary fiber 7.6 g
Fat 2.59 g
Saturated 0.27 g
Monounsaturated 0.58 g
Polyunsaturated 1.16 g
Protein 8.86 g

Vitamins Quantity %DV
Vitamin A equiv. 1 µg 0%
Thiamine (B1) 0.12 mg 10%
Riboflavin (B2) 0.06 mg 5%
Niacin (B3) 0.53 mg 4%
Vitamin B6 0.14 mg 11%
Folate (B9) 172 µg 43%
Vitamin B12 0 µg 0%
Vitamin C 1.3 mg 2%
Minerals Quantity %DV
Calcium 49 mg 5%
Iron 2.89 mg 22%
Magnesium 48 mg 14%
Phosphorus 168 mg 24%
Potassium 291 mg 6%
Sodium 7 mg 0%
Zinc 1.53 mg 16%
Other constituents Quantity
Water 60.21 g
Conclusion Garbanzo
Chickpeas are a good and easy source of having a lot of nutrients in a single dish. Some evidence has revealed that consumption of chickpea has benefited more than just providing basic nutrition. Consuming these may prevent the development and progression of many chronic diseases like cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes and many more. These also help in weight management.
Here at garden infograph we try to bring in front of you many relatable topics that are can add up to a healthy diet in your homes to keep your family and friends healthy. Some topics that we have covered are corn, giloy, edible flowers, cardamom, black pepper, cucumber, olive, groundnut, fennel and you will find many more. Health benefits of Tomatoes.
For pin:

 Garden infograph We provide our best experinces about plants
Garden infograph We provide our best experinces about plants